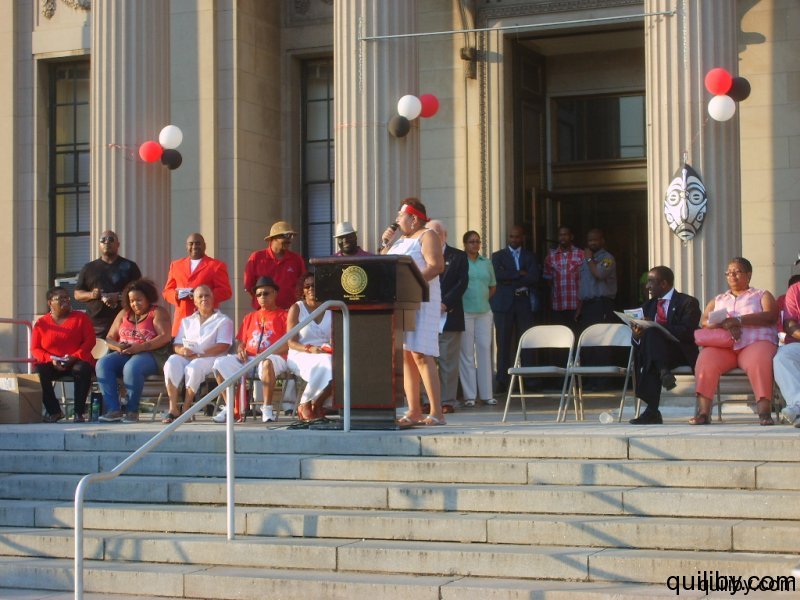
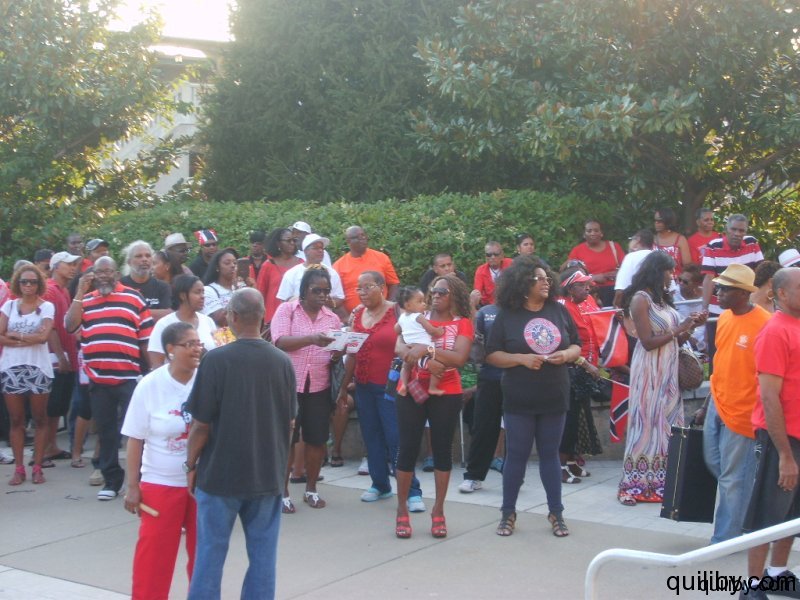
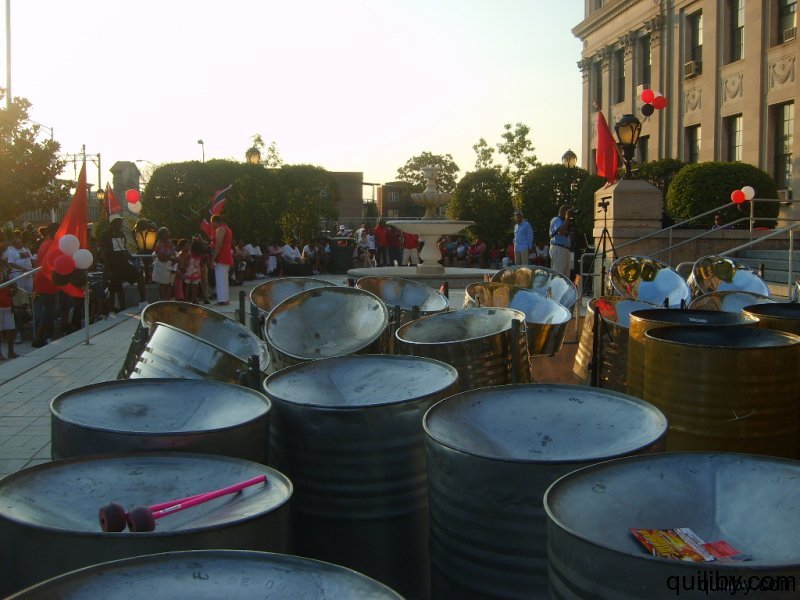
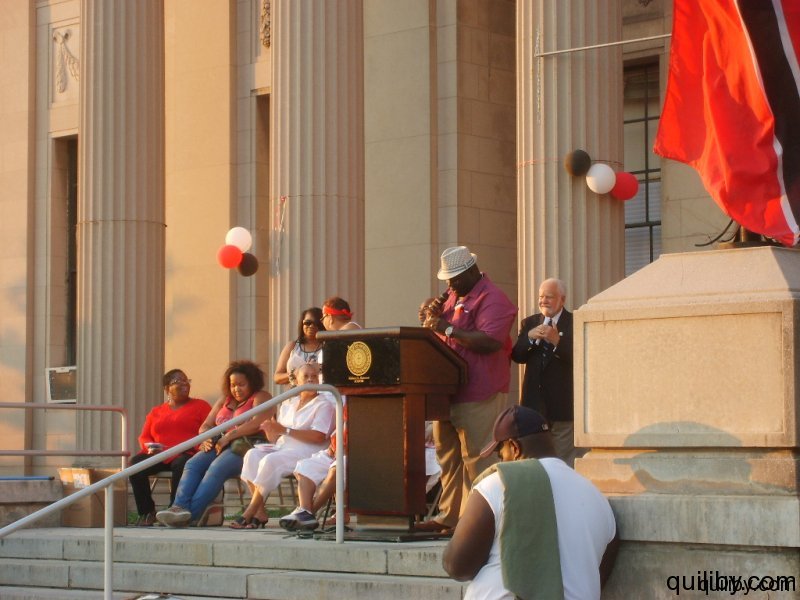
On August 31, 2012, the Sixth Annual Flag Raising ceremony was held in the city of East Orange, New Jersey to commemorate Trinidad and Tobago’s National Independence.
2012 marked the 50th anniversary of Independence for the twin-island Caribbean state and this gave additional significance to this year’s flag raising.
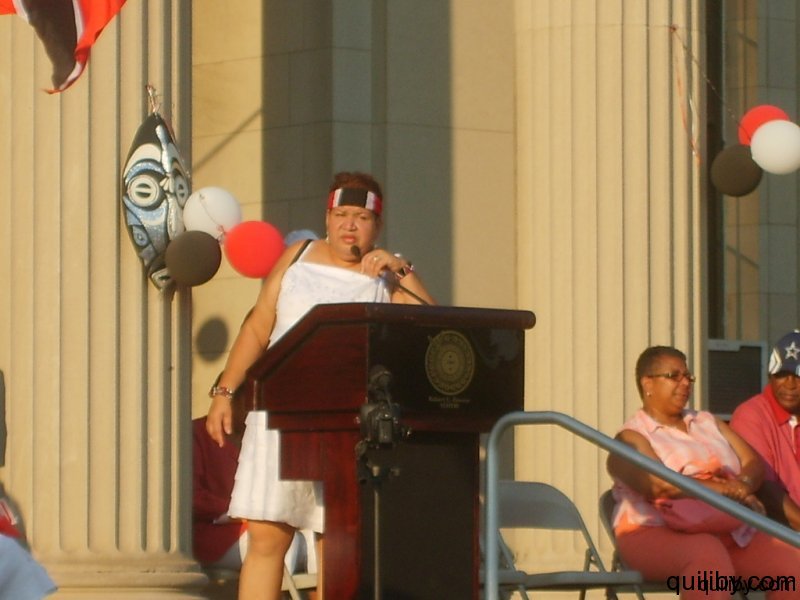
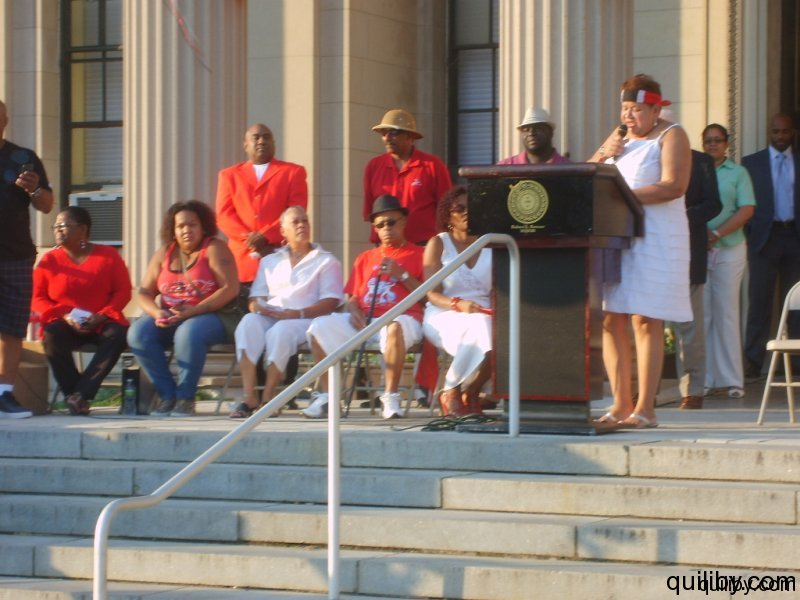
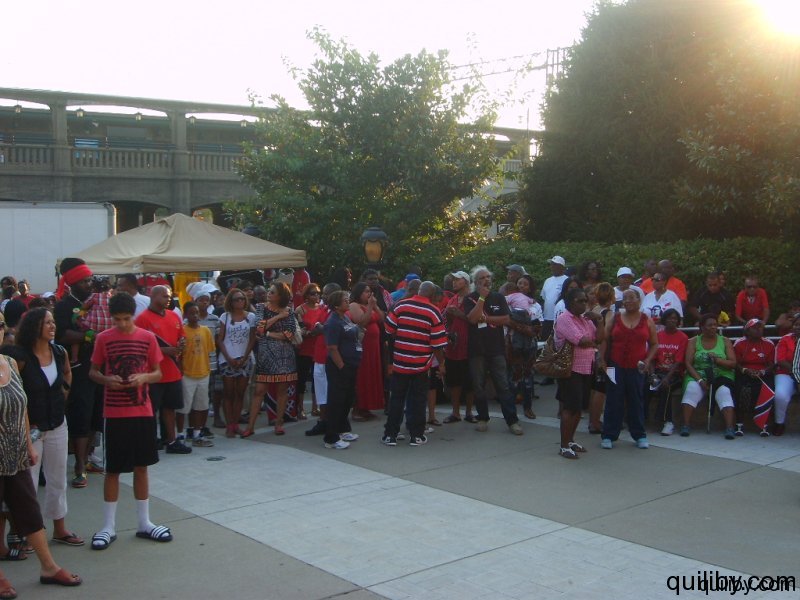
The event was led by Gail Bell-Bonnette, who has been at the forefront of Trinidad and Caribbean cultural activities in the Oranges. Trinidad and Tobago nationals from East Orange and surrounding cities such as Orange, Irvington, and Newark gathered in their hundreds to pay homage to the nation of their birth on the attainment of this jubilee milestone, having overcome slavery and colonialism.
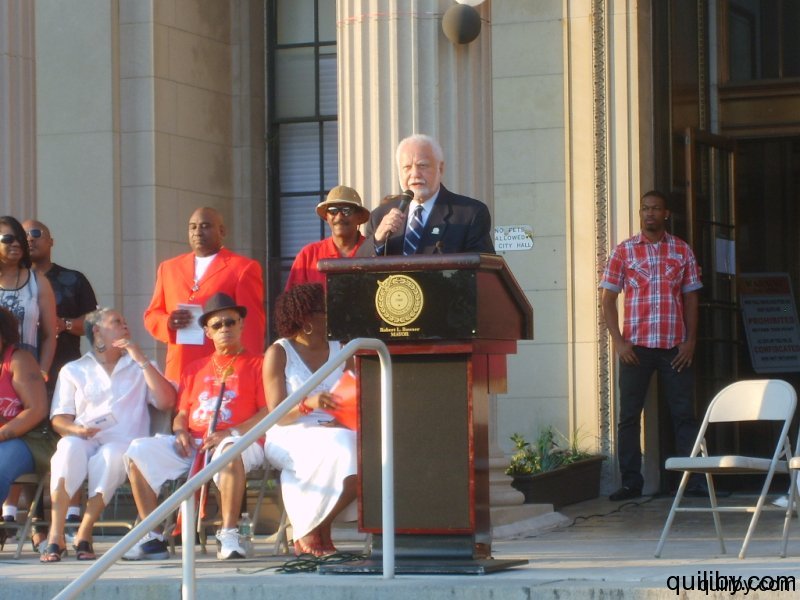
The Mayor of the City of East Orange, Mr. Robert Bowser, brought greetings to the festivities on behalf of himself and the City Council. He urged Trinidad and Tobagonians and all Caribbean nationals resident in the city to participate fully in the politics and general life of the city and to value education, which ensures the foundation for the protection of the freedom and liberties gained. The organizing committee, in conjunction with the New Jersey Carnival Committee, also presented awards to community activists and leaders for their contribution, dedication, and hard work towards the well-being of the Trinidadian community. Many of them had assisted in the East Orange Carnival, which was held for 21 years under the leadership of Gail Bell-Bonnette. In 2012, these faithful are making efforts to successfully re-institute the Carnival in the Oranges, New Jersey.
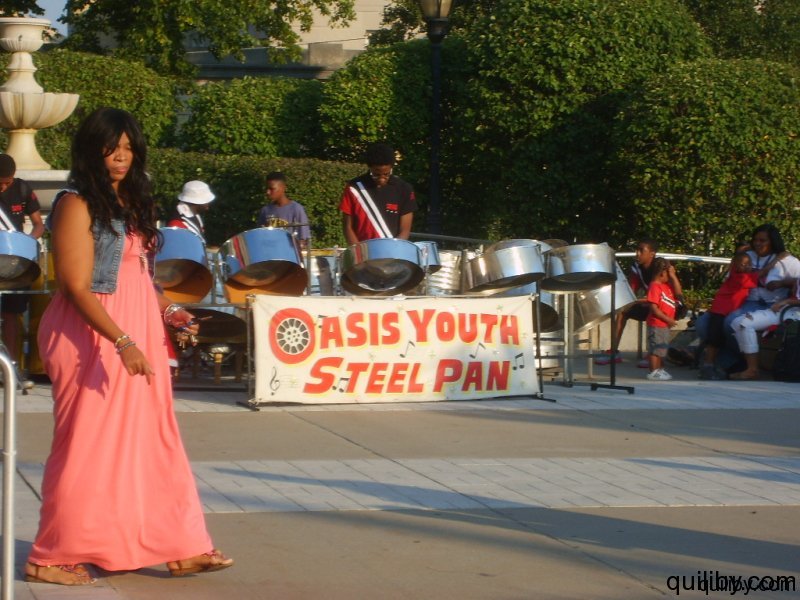
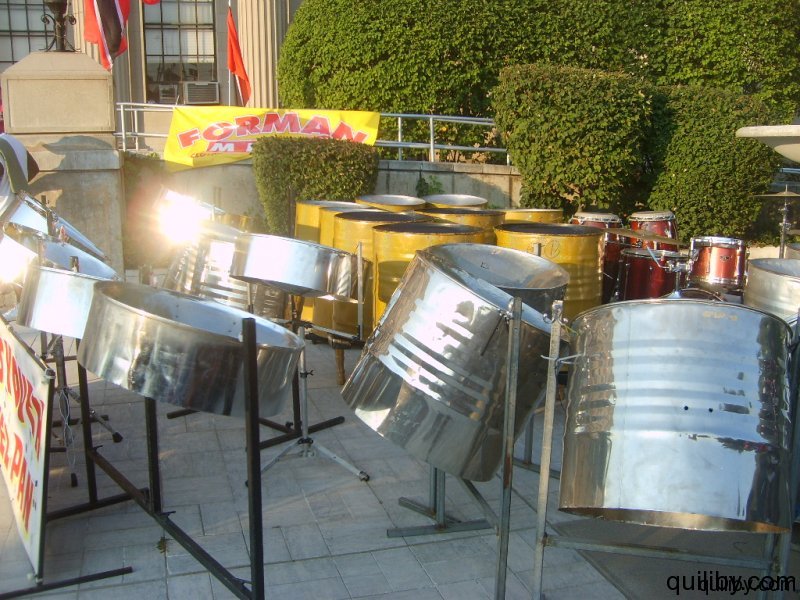
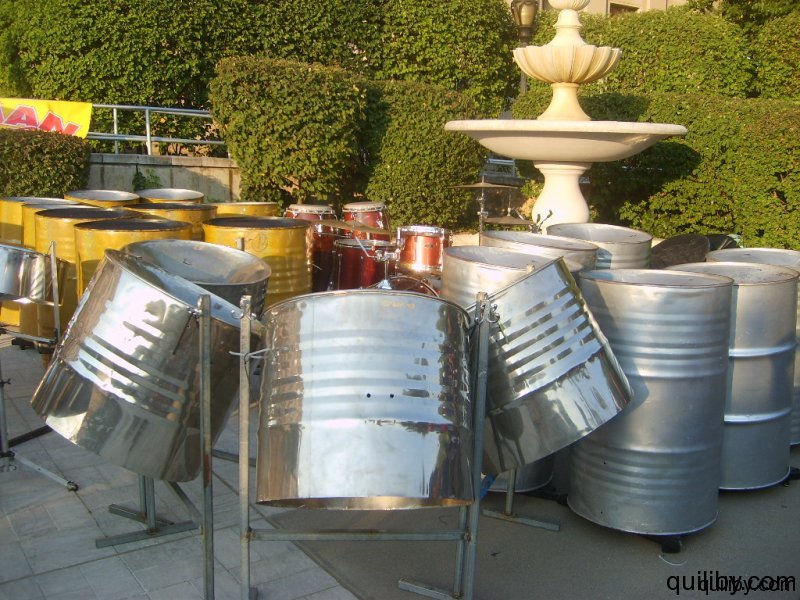
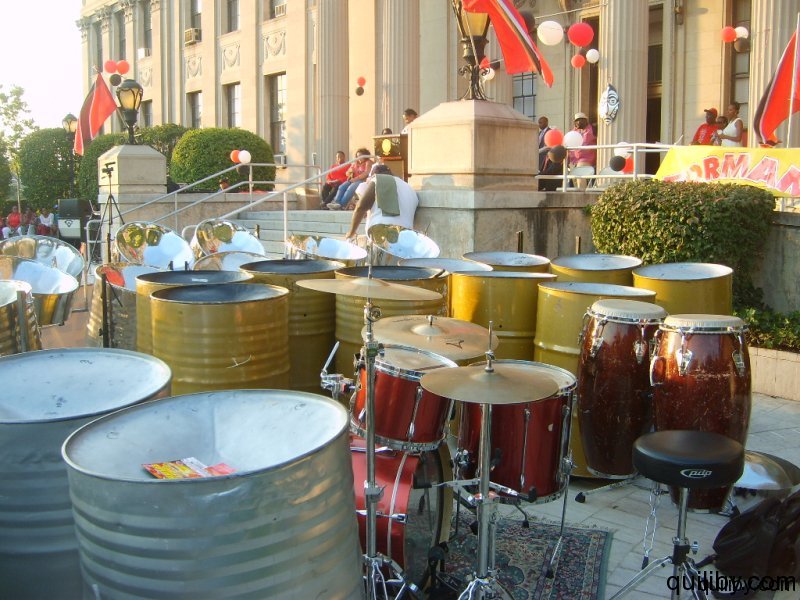
The crowd, which came out to witness and support the raising of the Trinidad and Tobago flag, was treated to the music of the Oasis Youth Steelband, a rhythm section, and DJ.